Tutorial 1
Implementation of Oracle ERP Supply Chain Planning and Procurement
Background
Company Hurd is a manufacturing company with annual sales of $100M. Over 20 years of marketing effort, the market share has increased tremendously to 20%.
Due to the expanding and dynamic market changes and business needs, management calls for a detailed study to further improve the market share. Hurd targets to increase market share by 10% 2 years after implementation.
Management intends to implement Enterprise Resource Planning (“ERP”) system Oracle to replace the current stand-alone legacy systems used by each individual functions or departments.
This Investment will provide advanced capabilities for communicating, planning, and optimizing supply and demand for all trading parties across all tiers of a supply chain.
For this project, company Hurd will implement Phase I for Planning and Procurement to be completed within 1 year time frame.
Project Organization Chart
Benefits of Oracle ERP
Supply Chain Exchange provides advanced capabilities for communicating, planning, and optimizing supply and demand for all trading parties across all tiers of a supply chain. Oracle Supply Chain Exchange provides the following benefits:
Reduced inventory levels
Normally, the inventory level is managed based on historical trends and this may have cost and revenue exposure due to over or under supply of inventory respectively. With ERP, it provides the collaborative tools to reduce inventory and free working capital. With clear communication and visibility extends to all trading partners, it allows companies to plan accordingly and is able to have a more predictable inventory level.
Improved visibility across entire supply chains
ERP provides collaborative capability to all trading partners across extended supply chains ensuring access to accurate and timely information. This visibility and easy access to information at any place or at any time, allows companies to work smarter and faster. It facilitates close collaboration between suppliers and supplier’s suppliers, customers and customer’s customers, at the most remote tiers of extended supply chains, transforming fragmented supply chains into responsive supply networks.
Increased velocity of information and material
The speed of the information and material moves between trading partners makes collaboration between companies at all tiers of a supply chain faster, easier and more reliable. Thus, the abilities to communicate in real-time increase the velocity of information and material across supply chain. This results in bottom line savings and increased customer satisfaction.
Improved ability to more accurately promise delivery
Being able to deliver as per promised to meet the customer demand is essential. ERP allows companies to see beyond their tier 1 suppliers to tier x suppliers. This level of visibility allows companies to identify problems, sooner rather than later, and to respond quickly ensuring that a promise made is a promise kept.
The current legacy systems lack the following functions and capabilities:
Collaborative Planning and Optimization
Oracle Supply Chain Exchange provides a common repository for cross-enterprise planning information (for example, demand, supply, and rules governing material flow between Exchange members). It provides message translation capabilities so that information can be uploaded to and downloaded from Oracle Supply Chain Exchange in a variety of formats.
Reduce Cycle Time with Holistic Planning
Optimization, planning, and scheduling of the entire supply chain is part of a holistic planning process. Oracle ASCP combines many elements of planning that have historically forced companies into multi-step planning processes resulting in longer planning cycles and multiple plans to reconcile. Oracle ASCP is able to generate holistic supply chain plans that simultaneously provide long range aggregate planning and short term detail scheduling.
It allows planning of material requirements, capacity requirements and replenishments for all facilities where inventories are stored or products are manufactured. Trading partner’s inventory locations and plants can also be included. Oracle ASCP allows the generation of the equivalent of Distribution Plans, multi-plant Master Schedules (Production Plans) and Material Requirements Plans (Manufacturing Plans).
Optimization for Planners
Oracle ASCP incorporates advanced optimization techniques. Using a simple and intuitive graphical user interface, planners can leverage advanced constraint-based solving technology to ensure that the plan is feasible and respects the constraints, including finite material and resource capacity, and project pegging. Thus, it is able to execute the plan and meet customer’s commitments. Rules can be defined to prioritize demands based on combinations of criteria such as dates, customer priorities, and item priorities. Objectives such as improving profitability or on time delivery performance can be achieved using Oracle ASCP.
Backward Compatibility and Multi-Instance Planning
Using Oracle ASCP, data can be planned from multiple instances and different versions of Oracle Applications. Collection programs let you automatically collect data from Oracle Applications instances on a net change basis. Current Oracle customers can implement Oracle ASCP without upgrading their other Oracle Applications. Interface tables also allow you to collect data from any legacy applications.
Plan the Supply Chain in a Centralized or Distributed Environment
Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning (ASCP) allows you to quickly and easily bring all functions within the enterprise into the planning process and enable critical information to flow throughout the global supply chain at Internet speed.
Common Data Model
Oracle ASCP and Oracle’s E-Business Suite share a common data model for planning and execution. And because aggregate planning and detailed scheduling are the same process, there is only one data model. One source of truth means a faster, simpler implementation, higher data integrity, and lower initial and long-term cost of ownership.
Advanced Simulation
Oracle ASCP provides online interactive simulation planning to rapidly simulate and respond to changing conditions. For example, an unconstrained plan and a constrained plan can be generated. Then compare the results based on the performance indicators. You can simulate the effects of changing sources, lead times, safety stocks, order modifiers, shipment methods, in-transit lead times, alternate components, alternate resources, and other planning data.
Increase Planners’ Efficiency with Instant Access to Global Supply Chain Information
Planners need to respond rapidly to a dynamic and complex environment. They need to have instant access to vast amounts of information including supply and demand information about the entire global supply chain. The Planner Workbench streamlines the common activities of planners, while providing easy access to the information needed to answer the tough questions faced by planners. Planners use intuitive customizable tree structures to display detailed information about a plan and get quick and easy access to frequently used information. The trees are organized based on the way work is assigned to planners. This makes access to information simple and intuitive. Distribution planners access information differently than manufacturing schedulers, who ask different questions than buyer-planners
Communicate Across the Extended Supply Chain with Internet-Based Collaborative Planning
Oracle ASCP extends the collaborative features of Oracle Applications. It is built on Oracle’s robust Internet architecture that allows all Oracle Applications to be deployed over the Internet or your corporate Intranet. It is also completely integrated with the other collaborative components of the Oracle E-Business Suite such as Oracle Internet Supplier Portal and Oracle Supply Chain Exchange. Oracle ASCP provides powerful Internet-based collaboration methods and allows you to communicate seamlessly with trading partners.
Oracle ASCP provides low cost web deployment of the entire advanced planning solution. Its architecture is compliant with open Internet standards and the data model is accessible through Java Business Objects and XML. This enables you to extend collaboration with Oracle’s web based adhoc query tools and OLAP tools, or any SQL-based query tool. Oracle’s Internet computing architecture provides an advanced framework for managing today’s collaborative supply chain.
Manage Your Global Supply Chain
Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning provides the tools to model and plan your entire supply chain. You can define all of your organizations or facilities including suppliers and customers. The relationships between organizations and the flow of materials can be defined through the supply chain using Sourcing Rules and Bills of Distribution.
Simultaneously Plan Material and Capacity
Oracle ASCP plans material and capacity requirements simultaneously. Run plans that are unconstrained by material and capacity (infinite planning) to determine resource and material capacity required to meet demand due dates. Alternatively, run plans constrained by material and resource capacity (finite planning) to schedule demand within material and resource constraints. Both material and resource constraint violations can be viewed in a single window and easily drill down to see details such as gross requirements, available supply (or capacity), and net requirements for the related materials or resources.
Plan across Manufacturing Modes in a Single Integrated Plan
Oracle ASCP supports full mixed mode manufacturing. It plan make to stock, make to order, assemble to order, and configure to order products simultaneously. Oracle ASCP is fully integrated with all Oracle Application manufacturing applications, including Oracle Discrete Manufacturing, Oracle Process Manufacturing, Oracle Shop Floor Management, Oracle Flow Manufacturing, and Oracle Project Manufacturing.
Oracle E-Business Suite—the Complete Solution
Oracle E-Business Suite enables companies to efficiently manage customer processes, manufacture products, ship orders, collect payments, and more—all from applications that are built on unified information architecture. This information architecture provides a single definition of the customers, suppliers, employees, products—all aspects of the business. Oracle E-Business Suite enables the sharing of unified information across the enterprise for better decision making with better information.
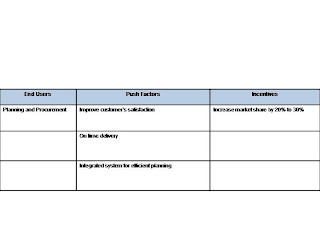
Push factors for implementation of Planning and Procurement
With the ERP implementation for planning and procurement, there will be an improvement in customer’s satisfaction due to better on time delivery. There is better inventory control due to accurate inventory tracking. Overall there is an integrated system for efficient planning which will benefit the company performance and delivery.
 Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder analysis refers to the action of analyzing the attitudes of stakeholders towards something (most frequently a project). It is used during the preparation phase of a project to assess the attitudes of the stakeholders regarding the potential changes.
Who are they?
PM – Project Manager
Proc – Planning and Procurement
Mgmt – Management Team (Sponsor)
Fin – Finance
IT – Information Technology
Prod - Production
Stakeholder Analysis Techniques: Mapping I: Position / Importance
Under the Problematic:
We target the stakeholder – Production is grouped under the Least Importance with the highest Oppose because they are at the lowest hierarchy, their mindset is still resistance to the change in adapting to the new system implementation.
Under the Antagonistic:
We target the stakeholder – Planning & Procurement is grouped under the Most Antagonistic with the highest oppose because they will higher bargaining power because they have more problem to face and data to console during the implementation so they are resistance to the change in adapting to the new system implementation.
Under the Supporter:
We target the stakeholder –Finance, Mgmt and PM as they will support the implementation of the Oracle as more revenue and greater benefit will be generated after the implementation. IT also supports as they are the first to start-up with the project and involve in the changes and training in the System.
Stakeholder Analysis Techniques: Mapping II: Power / Predictability
Under the Unpredictable but manageable Response:
We target the stakeholder – Production is grouped under the least Power and low predictability because they will just follow accordingly to the schedule changes from higher level
Under the Powerful but Predictable:
We target the stakeholder – IT, management and Finance is grouped under the highest Power and high predictability because they will experience the most impact if there is any issue during the implementation and they have the final say in the decision making.
Under the Greatest Danger or Opportunity:
We target the stakeholder – Planning and Procurement is grouped under the High Power and low predictability because they are in a position to block or support new programs. This stakeholder may test out the project process with other stakeholders prior to detailed execution.
Stakeholder Analysis Techniques: Mapping II: Power / Interest
Under Minimal Effort:
We target the stakeholder – Production is grouped under the Low Power and lack of interest because they are just follow instruction from the Management
Under the Keep Informed:
We target the stakeholder –Planning & Procurement is grouped under low Power and high level of interest because they more interested in the progress of the implementation
Under the Key Player:
We target the stakeholder – IT, Finance and Management is grouped under the high Power and high level of interest because they need to ensure the successful implementation of the project and to resolve any issue faced during the implementation
For Key Player, these stakeholders should be given primary consideration before any decision is made.
Project constraints: Performance, time and resources Trade offs
During the implementation, the project manager needs to consider the scope and cost trade off when an unexpected problem occurs.
The performance of the project must be reliable and accurate as it will affect the overall organization performance. This cannot be compromised while adjustment may still be able to be made on the budget and time of the project. It is still acceptable if the cost does not exceed 20% of the budget and is behind schedule by 6 months.
Ownership, commitment and involvement from the top management are important. A clear direction is embraced at all levels and top management to support the project team with the necessary resources until the project is completed.
The right selection of software is the key to successful implementation. If the software is chosen wrongly, it will be difficult for the software vendor to implement correctly accordingly to your business processes.
Organization should follow accordingly to defined implementation process steps given by the experts. During implementation, organizations might come to know about some functionality and would want to add those functionalities at the same time. There is a need to discuss with the experts for any process changes. If not, this may have an impact on the project cost and schedule.
An effective change management strategy and plan is required to cater for the transition from the legacy to the new Oracle world. This is important as the workflow and responsibilities will be different.
Organization should check the track record of vendor implementation partner. They may ask the vendor for client visit to see the running software and its functionalities
There should be awareness, capability and motivation at all levels among all stakeholders.
There is necessary infrastructure available for the effective implementation of the system.
Responsibilty Matrix
Legend:
R – Responsible
A – Accountable
C – Consulted
I – Informed
PM – Project Management
Log – Logistics
Proc – Procurement and Planning
WH – Warehouse
Mgmt – Management
Fin – Finance
IT – Information Technology
Prod - Production
Tutorial 2
Mind Mapping Exercise
The mind mapping diagram shows an overview of the processes for the ERP implementation.
The team has identified 8 main stakeholders, mainly the Management, Vendor, Sales and Marketing, Finance, IT, Production, Planning and Procurement, Logistics for the implementation. Phase 1 implementation will be on Planning and Procurement.
Tutorial 3
Work Breakdown Structure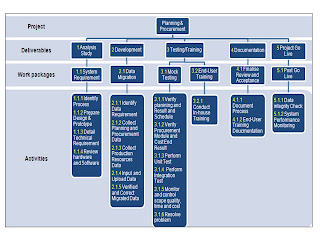 Tutorial 4
Tutorial 4
Project Costing
Initial Project Costing Breakdown
Implementation of ERP Planning and Procurement activities on nodes -Network Diagram and Critical Path Analysis
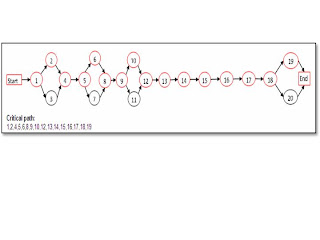
The critical path is from 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9,10,12,13,14,15,15,16,17,18,19
Start and Finish Network Computation
CPA Activities - Initial Plan
Initial Schedule – Gantt Chart
Tutorial 5
SWOT Analysis for the implementation of Oracle Planning and Procurement
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning used to evaluate the strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats which involved a project. Company Hurd uses SWOT analysis for evaluation after the implementation of the ERP for planning and procurement.
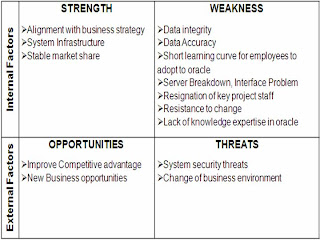
***From SWOT Analysis, we derived that most of risk are cause by internal factors which fall under the weakness portion.
STRENGTH:
Alignment with business strategy - by implementation of Oracle allows company to generate more revenue, profits and operation efficiency.
System Infrastructure – readiness of system Infrastructure such as network connection, IT team, Hardware and software support in the implementation of Oracle
Stable market share – with strong financial figure will attract more investors. We can have more budgets in the implementation of Oracle.
WEAKNESS:
Data integrity – data interface issue due to complexity of input data. Transmission of the data from spreadsheet into system or download from system might cause discrepancy in the data retrieve.
Data Accuracy - data input by the end users for the data migration must be accurate as it will affect the end result.
Short learning curve for employees to adopt to oracle - due to tight training schedule, employee will have difficulty in master the system. With the new implementation of Oracle, a lot of work flow process is being changed from manual to systemization.
Server Breakdown, Interface Problem – due to increase in the flow of data which lead to traffic data overflow, if system is unable to support will cause server breakdown. Interface problem can be caused by the user if they have input the wrong sequences which validate the system.
Resignation of key project staff – will mess up the schedule if the handover job are not done properly.
Resistance to change - employees may not want to adopt and learn new changes. Longer time and resources may be taken to train the staffs.
Lack of knowledge expertise in oracle – everyone are new to oracle need more time to explore. IT personnel might be new to process system and interface sequence.
OPPORTUNITIES:
Improve Competitive advantage – utilize the resources and deliver the same benefit as the competitive but at a lower cost. This would create competitive advantages so as to create value to our customers and generate more profit.
New Business opportunities – by capture new market opportunities so as to increase the market share. The company is able to respond fast to customer’s dynamic needs after the Oracle implementation.
THREATS:
System security threats – data privacy, authentication or even subject to virus attack.
Change of business environment - pose a threat to financial figure which will affect the company’s ability to sponsor the project due to tight financial constraint.
Risk Analysis for the implementation of Oracle Planning and Procurement
After the SWOT analysis and assessment, we have identified the top 5 risk events. The risk are Prepare design & prototype, Planning & procurement data collection, Verify planning end result & schedule, review hardware & software and Project go live which is shown in the risk response matrix
Risk Response Matrix
It is further identified to 2 top risk events which is Planning & procurement data collection and Verify planning end result & schedule.
Impact and Probability Matrix
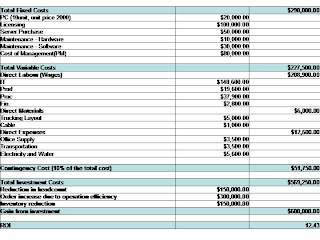
Project Costing – Initial versus Delay Cost Summary
CPA Activities - Delay in Schedule Plan
Delay Schedule –Gantt Chart
With the assumption that there will be a 48 days delay each in Planning & procurement data collection and Verify planning end result & schedule events, we have reviewed the Critical Path Analysis. The overall project schedule is delayed by 96 days with the critical path remains unchanged. The overall schedule has been delayed from 196 to 292 days per the Earliest Finished Date.
The critical path is from 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9,10,12,13,14,15,15,16,17,18,19
Due to the delay, the investment cost has increased by 1.45% from $569k to $577K which is mainly due to the additional direct labour and contingency cost. As such, ROI has reduced from 12.4% to 10.8% and the breakeven duration has increased from 1 to 1.16 years.
Conclusion
With the Oracle Supply Chain Planning and Procurement implementation, the company can work efficiently through the development and implementation to quickly achieve business results.
Tutorial 6
Implementation of ERP Oracle Supply Chain Planning and Procurement
Project Handover
Project Management: Finalization phase
Project Handover Report -> Project Completion Report
Prepared by : Eng Chew Peng
Title : Project Manager
Location : Yishun Building 1
Version No : 1.0
Version Date : 1 Aug 2010
Status : Draft/Final review/Sign off
DMS ref no. : NA
File/Doc no. : NA
Document control sheet
Contact for enquiries and proposed changes
If you have any questions regarding this document or if you have a suggestion for Improvements, please contact:
Project Manager : Eng Chew Peng
Phone : +65 98889999
Project Handover approval
The following officers have approved this document.
Sponsor
Name : Mr Hurd on behalf of Management Team
Position : Managing Director
Signature : Date :
The following officer endorsed this document.
Name : Eng Chew Peng
Position : Project Manager
Signature : Date :
Project Team Member:
Liew Sok Ying
Steven Khoo
Christine Teo
Project Performance
The project has been implemented successfully with no major system performance issues.
Overall, the activities have been delayed by 96 days due to a delay in 2 of critical activities. Thus, this has affected the project completion and has also used up the contingency cost factored in for this project. After taking into consideration of the contingency cost, the project has exceeded by $8.25K.
Operational Handover
Overview of Impacts
The gain from this investment outweighs the investment cost due to an increase in the productivity and operation efficiency. As such, this results in a reduction in the labour and inventory costs.
Risk
Data accuracy and integrity continues to be an on-going issue which requires the efforts of all departments to ensure proper data updating and transmission.
Handover
The first major phase in delivering a successful ERP implementation is to define the actual goals of the project. This involves identifying and documenting the features and functionality delivered during the implementation phase of the project.
As the project proceeds, there is a need to review the documented requirements lists to check that the current progress in the direction of the project. Without the documented requirements, it will be difficult to manage as new and unexpected changes creep into the project’s implementation.
There should be a constant follow up on the long term maintenance support.




















